Grade 2 osteochondrosis of the cervical spine requires professional treatment. With the development of this pathology, the integrity of the intervertebral discs is compromised and the space between them is reduced. Of all the forms of osteochondrosis, cervical is the most common. The neck is mobile, in this regard, it is constantly stressed. The initial stage of osteochondrosis is normally tolerated. Started - poses a great threat to health.
Why does cervical spine osteochondrosis occur?
There are many causes of cervical osteochondrosis. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle may develop pathology. The arteries pass through the vertebrae of the cervical region and supply blood to the arteries of the brain. Osteochondrosis SHOP often occurs due to increased stress on the neck. Grade 1 spinal osteochondrosis occurs in young and old people. An important role is played not by age, but by the lifestyle and characteristics of the body.
Grade 2 cervical osteochondrosis is more common in adolescents. There is a concept of "adolescent osteochondrosis" in medicine. A common cause of grade 1 or 2 osteochondrosis is a misalignment of the head. As the disease progresses, the pulp breaks. The types of osteochondrosis depend on how pronounced the pulp hernia is. Timely treatment of primary osteochondrosis leads to the progression of the pathological process. In the third stage of the disease, degenerative-dystrophic processes are pronounced: the patient is more concerned about back and neck pain.
Features of the first stage
With grade 1 cervical lumbar osteochondrosis, the pathological process extends to the muscles. The initial stage is characterized by the formation of cracks in ring fibrosis. Contains collagen fibers
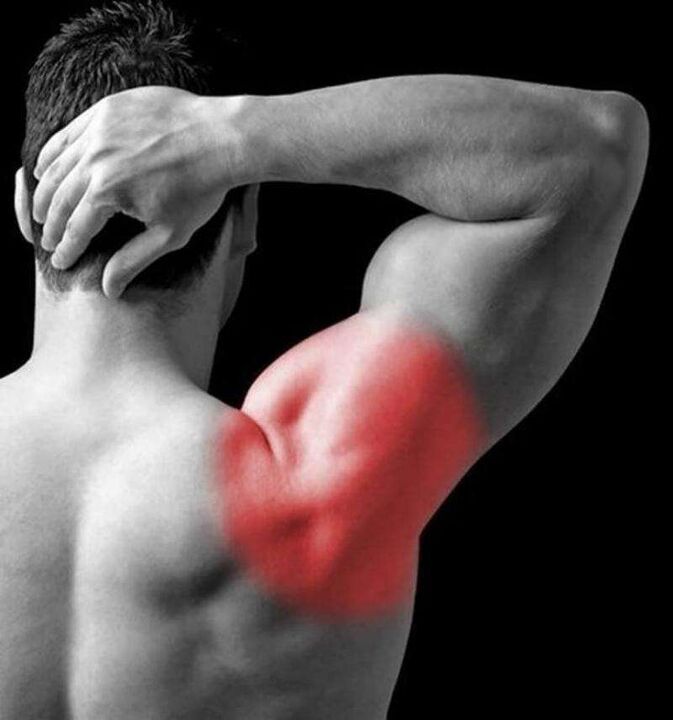
Grade 1 osteochondrosis of the cervical spine causes unpleasant symptoms:
- The first stage of osteochondrosis is characterized by pain in the back of the head. Some people swell. Severe cramping pain may appear with grade 1 cervical osteochondrosis.
- If a person is diagnosed with cervical lumbar osteochondrosis, he should consult an ophthalmologist. Students can expand.
- Grade 1 cervical osteochondrosis often causes Wright syndrome. If the patient puts his hand behind his head, the pain intensifies.
- Cervical syndrome usually develops at the beginning of the disease. In this case, the inflammation affects the muscles. The progression of cervical syndrome is associated with abscess. A person begins to feel pain in the neck, limited mobility of the joints.
- In the first stage, anterior scalene muscle syndrome may appear, in which case the subclavian artery is affected.
How is the treatment performed? The goal of therapy is to repair pulp hernias and prevent unpleasant symptoms. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is treated surgically. The duration of the postoperative period is 7 days. In a month or two, the stitches gradually grow together.
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to wear a special collar, which is worn around the neck. The doctor recommends the use of calcium gluconate solution. The remedy helps wounds to heal.
What happens in the second stage of the disease?
Secondary cervical lumbar osteochondrosis develops at an early stage with ineffective treatment. Inflammatory reactions manifest themselves, the intervertebral foramen is reduced.
Grade 2 cervical osteochondrosis causes osteophytes. These are skeletal processes that occur against the background of dehydration.
Stage 2 cervical osteochondrosis can last 4-5 years. The disease periodically decreases and worsens. A characteristic feature of the disease is dizziness syndrome.
Treatment consists of hand therapy. The goal is to provide the cervical muscles with normal fixation. Depending on the condition, orthopedic treatment (closure of the vertebrae) may be prescribed. Drug treatment is required. Calcium chloride is prescribed to relieve pain. Therapeutic gymnastics is recommended: 30 minutes a day. The main load should be on the joints.
How does the third stage manifest itself?
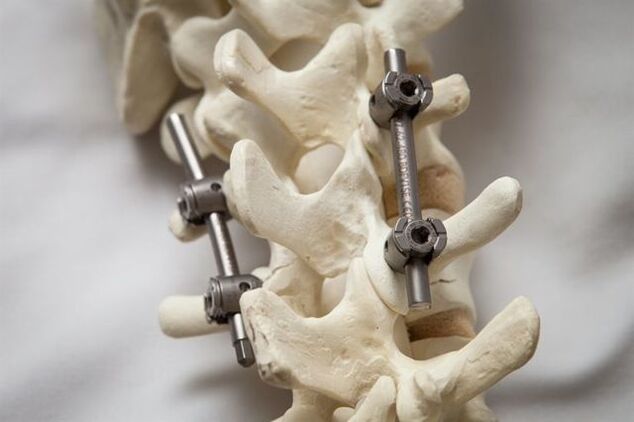
Tertiary osteochondrosis is very difficult to treat. With this disease, the structure of the intervertebral discs changes.
The pathological process involves tissues and joints:
- The vertebral body is torn, there are characteristic signs of an intervertebral hernia. The person begins to feel severe pain in the back, neck and limbs. Degenerative-dystrophic reactions affect a large part of the neck.
- Third-degree osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is characterized by vestibular disorders. Periodically, a person experiences pain in the temples. Some patients may be partially unconscious.
- In the third stage, the danger of the disease is that it leads to endocrine pathology. Therapy involves the use of surgery and hand techniques. No drugs are prescribed in the third stage of cervical osteochondrosis.
- The patient may have polysegmental osteochondrosis. With this disease, cervical lumbar segments are affected, shoulder mobility is impaired, and pain appears in the elbows.
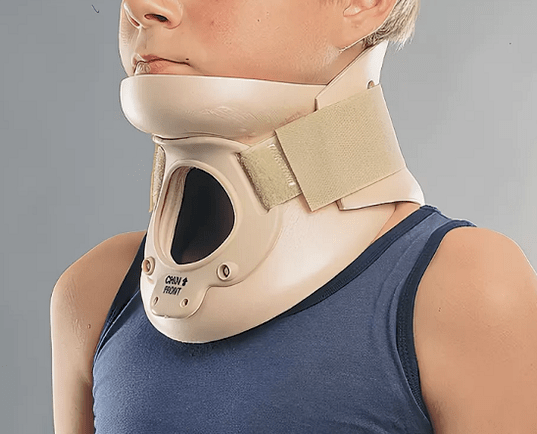
It is necessary to wear a necklace to restore the function of the spine.
Disease syndromes
Cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by syndromes:
- Occurs when vertebral, cartilage and bone tissue are involved in a pathological process. Neck mobility is impaired. If a person tries to turn his head to the side, pain appears in the occipital region of the neck. The vertebrae undergo morphological changes seen on radiography. The symptoms of a syndrome are interrelated. An important symptom of vertebral syndrome is morphological changes in cartilage tissue and bone structures. This syndrome is difficult to diagnose. A similar symptom complex is present in myositis.
- Vertebral artery syndrome is another manifestation that can occur regardless of the degree of cervical osteochondrosis. The pathological process affects the blood vessels that feed the brain. From time to time there is a feeling of wonder. Vertigo is a symptom of vertebral artery syndrome. Blood pressure may jump, there is occasional nausea and vomiting. Nerve endings are irritated, which causes headaches. Fainting and oxygen starvation are possible with vertebral artery syndrome. The disease is accompanied by the collapse of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
- Heart syndrome manifests itself with pain in the sternum. Rapid fatigue and decreased performance are observed. The heart beats faster. Diagnosis includes angiography and functional tests. Radicular syndrome is associated with damage to the spinal nerves. It is one-sided. With radicular syndrome, neck pain is observed, combined with paralysis.
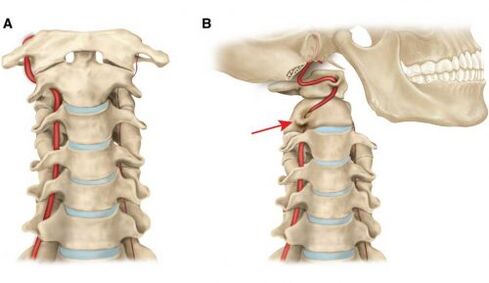
It should be noted that osteochondrosis damages many vertebrae.
What is osteochondrosis of the thoracic region?
Thoracic lumbar osteochondrosis is found in young and old people: there is no age difference. Causes degenerative-dystrophic changes in pathological cartilage and bone structures. Delayed treatment leads to disruption of the structure of ligaments, joints, intervertebral discs. At an advanced stage, thoracic osteochondrosis leads to the destruction of intervertebral discs.
Complications of the disease can be:
- pneumosclerosis;
- infertility;
- malignant formations.
If the disease develops in a young person, premature aging of the musculoskeletal system is observed. The functioning of cartilage structures and tissues is significantly impaired.
Clinical manifestations and causes
- With the development of this pathology, chest pain appears. Occurs in a calm state and while driving. Unpleasant feelings intensify after lifting weights and sharp turns.
- The disease manifests itself by squeezing from behind. As a result of this problem, breathing is impaired.
- Colds can occur.
- Some people complain of peeling skin and thinning of the nail plate.
The disease is associated with pathological reactions in the intervertebral discs. It can be inherited. The factor that prevents it is the defeat of the intervertebral discs. In some people, the disease is diagnosed on the background of osteophytes. The reason may be less physical activity or, conversely, physical inactivity.
Therapeutic activities
If there are no neurological symptoms, complex treatment is still required. Therapy can not be postponed, otherwise the destruction of the intervertebral discs will occur.
It is necessary to make a diagnosis before starting treatment. If a person detects at least one of the above symptoms, he should consult a neurologist. The doctor will take a medical history and examine the thoracic region. Herniated discs are detected on palpation. If the doctor finds it, he will schedule an additional examination. Radiography is required. The MRI procedure allows you to study the musculoskeletal system and identify neoplasms.
Treatment depends on the degree of osteochondrosis of the breast; begins after the diagnosis is confirmed. The doctor prescribes drugs that help relieve pain and restore the function of the musculoskeletal system. In order to treat this pathology, injections, physiotherapy, physiotherapy exercises are needed. Additional procedures - magnetotherapy, vacuum therapy, physiotherapy exercises.
Daily exercise has a complex effect on the body, improves the functioning of the musculoskeletal system and respiratory system. Massage reduces the severity of pain, increases muscle tone, relieves fatigue and improves blood circulation in the tissues. The procedure is performed by an experienced specialist.
The result
How many years can you live with cervical and thoracic lumbar osteochondrosis? The pathology is not life threatening, but the symptoms are a serious concern. The clinical picture of the disease can change: it all depends on the effectiveness of treatment.